반응형
DFS(Depth - First Search)와 BFS(Breadth - First Search)
그래프 탐색
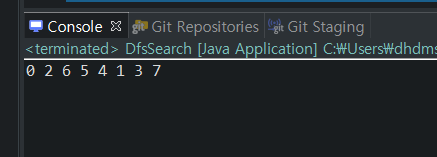
DFS: Stack으로 구현, 깊이 우선 탐색
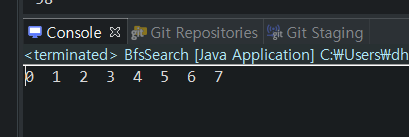
BFS: Queue로 구현, 넓이 우선 탐색
그래프를 matrix로 표현하기
package algorism.ch04;
public class UndirectedGraph {
private int count;
private int[][] vertexMatrix;
// 몇개 짜리 그래프인지 생성자로 받는다.
public UndirectedGraph(int count) {
this.count = count;
// count만큼의 2차원 배열을 만든다.
vertexMatrix = new int[count][count];
}
// 간선의 유무, 간선 정보를 처리하는 함수
public void addEdges(int from, int to, int weight) {
vertexMatrix[from][to] = weight;
vertexMatrix[to][from] = weight;
}
public int[][] getMatrix() {
return vertexMatrix;
}
}
깊이 우선 탐색(DFS)
- 인접한 노드를 우선 탐색하는 방식
- 스택을 활용하여 구현할 수 있음
- DFS탐색 순서: 0 - 1 - 3 - 7 - 4 - 5 - 2 or 0 - 2 - 6 - 5 - 4 - 1 - 3 - 7
package algorism.ch04;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DfsSearch {
int count;
// 방문 유무 변수
boolean[] visitied;
Stack<Integer> stack;
int[][] matrix;
public DfsSearch(int count) {
this.count = count;
visitied = new boolean[count];
stack = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void dfsTraversal() {
stack.push(0);
visitied[0] = true;
while (stack.isEmpty() == false) {
// 꺼냄
int node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node + " ");
for(int j = 0 ; j < count; j++) {
if(matrix[node][j] != 0 && visitied[j] == false) {
// 인접한 요소를 넣어준다.
stack.push(j);
visitied[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 그래프 그리기
int count = 8;
UndirectedGraph graph = new UndirectedGraph(count);
graph.addEdges(0, 1, 1);
graph.addEdges(0, 2, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 3, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 4, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 6, 1);
graph.addEdges(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(3, 7, 1);
DfsSearch dfs = new DfsSearch(count);
dfs.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
dfs.dfsTraversal();
}
}
너비 우선 탐색(BFS)
- 한 노드에 모든 인접한 노드를 탐색하는 방식
- 큐를 활용하여 구현할 수 있음
- BFS 탐색 순서: 0 - 1- 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7
package algorism.ch04;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class BfsSearch {
int count;
boolean[] visited;
ArrayList<Integer> queue;
int[][] matrix;
public BfsSearch(int count){
this.count = count;
visited = new boolean[count];
queue = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
public void bfsTraversal() {
queue.add(0);
visited[0] = true;
while(queue.size() != 0) {
int node = queue.remove(0);
System.out.print(node + " ");
for(int j = 0; j<count; j++) {
if(matrix[node][j] != 0 && !visited[j] ) {
queue.add(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 8;
UndirectedGraph graph = new UndirectedGraph(count);
BfsSearch bfsSearch = new BfsSearch(count);
graph.addEdges(0, 1, 1);
graph.addEdges(0, 2, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 3, 1);
graph.addEdges(1, 4, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(2, 6, 1);
graph.addEdges(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdges(3, 7, 1);
bfsSearch.matrix = graph.getMatrix();
bfsSearch.bfsTraversal();
}
}
참고 사이트
https://mygumi.tistory.com/102
[그래프] DFS와 BFS 구현하기 :: 마이구미
이번 글은 자료구조 중 그래프를 다뤄본다. 백준 알고리즘 1260번을 통해 진행하니 참고하길바란다. 그래프는 정점과 간선으로 이루어진 자료구조의 일종이다. G = (V, E) 그림을 보다시피, 정점과
mygumi.tistory.com
반응형