반응형
큐 특징
- 맨 앞(front)에서 자료를 꺼내거나 삭제하고, 맨 뒤(rear)에서 자료를 추가 함
- First In First Out (선입선출) 구조
- 일상 생활에서 일렬로 줄 서 있는 모양
- 순차적으로 입력된 자료를 순서대로 처리하는데 많이 사용 되는 자료 구조
- 콜센터에 들어온 문의 전화, 메세지 큐 등에 활용됨
- JDK 클래스: ArrayList
연결 리스트를 이용한 예제
package ch40;
public class MyListNode {
private String data; // 자료
public MyListNode next; // 다음 노드를 가리키는 링크
public MyListNode(){
data = null;
next = null;
}
public MyListNode(String data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public MyListNode(String data, MyListNode link){
this.data = data;
this.next = link;
}
public String getData(){
return data;
}
}
package ch40;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class MyLinkedList {
private MyListNode head;
int count;
public MyLinkedList()
{
head = null;
count = 0;
}
public MyListNode addElement( String data )
{
MyListNode newNode;
if(head == null){ //맨 처음일때
newNode = new MyListNode(data);
head = newNode;
}
else{
newNode = new MyListNode(data);
MyListNode temp = head;
while(temp.next != null) //맨 뒤로 가서
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = newNode;
}
count++;
return newNode;
}
public MyListNode insertElement(int position, String data )
{
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
MyListNode newNode = new MyListNode(data);
if(position < 0 || position > count ){
System.out.println("추가 할 위치 오류 입니다. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return null;
}
if(position == 0){ //맨 앞으로 들어가는 경우
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
}
else{
MyListNode preNode = null;
for(i=0; i<position; i++){
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
newNode.next = preNode.next;
preNode.next = newNode;
}
count++;
return newNode;
}
public MyListNode removeElement(int position)
{
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
if(position >= count ){
System.out.println("삭제 할 위치 오류입니다. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return null;
}
if(position == 0){ //맨 앞을 삭제하는
head = tempNode.next;
}
else{
MyListNode preNode = null;
for(i=0; i<position; i++){
preNode = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
}
count--;
System.out.println(position + "번째 항목 삭제되었습니다.");
return tempNode;
}
public String getElement(int position)
{
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
if(position >= count ){
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류 입니다. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return new String("error");
}
if(position == 0){ //맨 인 경우
return head.getData();
}
for(i=0; i<position; i++){
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return tempNode.getData();
}
public MyListNode getNode(int position)
{
int i;
MyListNode tempNode = head;
if(position >= count ){
System.out.println("검색 위치 오류 입니다. 현재 리스트의 개수는 " + count +"개 입니다.");
return null;
}
if(position == 0){ //맨 인 경우
return head;
}
for(i=0; i<position; i++){
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return tempNode;
}
public void removeAll()
{
head = null;
count = 0;
}
public int getSize()
{
return count;
}
public void printAll()
{
if(count == 0){
System.out.println("출력할 내용이 없습니다.");
return;
}
MyListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null){
System.out.print(temp.getData());
temp = temp.next;
if(temp!=null){
System.out.print("->");
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if(head == null) return true;
else return false;
}
}
package ch43;
import ch40.MyLinkedList;
import ch40.MyListNode;
interface Queue{
public void enQueue(String data);
public String deQueue();
public void printQueue();
}
public class MyListQueue extends MyLinkedList implements Queue{
MyListNode front;
MyListNode rear;
public MyListQueue()
{
front = null;
rear = null;
}
public void enQueue(String data)
{
MyListNode newNode;
if(isEmpty()) // 비어있는지 확인 (처음으로 들어가는 경우)
{
newNode = addElement(data);
front = newNode;
rear = newNode;
}
else // 맨 뒤로 들어가는 경우
{
newNode = addElement(data);
rear = newNode;
}
System.out.println(newNode.getData() + " added");
}
public String deQueue()
{
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
return null;
}
String data = front.getData();
front = front.next;
if( front == null ){
rear = null;
}
return data;
}
public void printQueue()
{
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("Queue is Empty");
return;
}
MyListNode temp = front;
while(temp!= null){
System.out.print(temp.getData() + ",");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
package ch43;
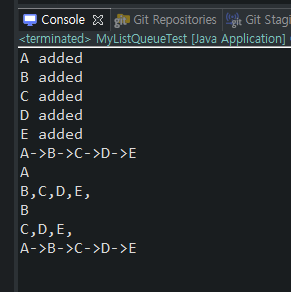
public class MyListQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyListQueue listQueue = new MyListQueue();
listQueue.enQueue("A");
listQueue.enQueue("B");
listQueue.enQueue("C");
listQueue.enQueue("D");
listQueue.enQueue("E");
listQueue.printAll();
System.out.println(listQueue.deQueue());
listQueue.printQueue();
System.out.println(listQueue.deQueue());
listQueue.printQueue();
listQueue.printAll();
}
}
반응형
'언어 > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 제네릭 메서드 (0) | 2021.05.02 |
|---|---|
| 제네릭(Generic) (0) | 2021.05.02 |
| 스택(stack) (0) | 2021.04.26 |
| 연결 리스트(LinkedList) (0) | 2021.04.26 |
| 배열(Array) (0) | 2021.04.26 |



